Last updated on October 9th, 2023 at 01:03 pm

Mutual Fund investment is becoming popular by each day, but choosing a right Mutual Fund is also getting harder as there are handful of options to choose from.
Here we will help you to understand various types of mutual fund. It is important to understand various types of mutual funds and their characteristics for choosing a right scheme for you.
As per SEBI mutual funds are classified as below
Classification Based on Organization structure
1. OPEN ENDED SCHEMES
2. CLOSE ENDED SCHEMES
3. INTERVAL
OPEN ENDED SCHEMES
In this scheme purchase and selling of units are open at any time, as the new investors bring fund, new units are added to the fund.
Thus there is an unlimited units are available in this scheme.
CLOSE ENDED SCHEMES
In this scheme purchasing a unit happens only during scheme’s initial period decided by AMC called New Fund Offer(NFO).
No new units are issued after NFO, but the trading of existing units is possible through stock market.
This scheme has a fixed maturity period on which the repayment is done based on the Net Assets Value (NAV).
Before maturity the units can be sold through stock exchange like publicly trading stocks.Also some AMC allows to exit before maturity by purchasing.
INTERVAL
In this scheme units are sold during a specific period similar to Close Ended Scheme.But AMC can allow this transaction period multiple time when need arises.
The transaction period can not be more than 2 days. And there should be 15 days gap between two transaction period.
Classification Based on Investment Portfolio
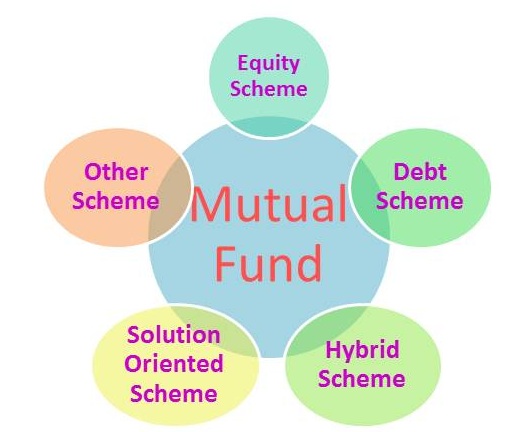
AMC is classifying mutual funds based on investment portfolio of the Scheme.
1. EQUITY SCHEMES
2. DEBT SCHEMES
3. HYBRID SCHEMES
4. SOLUTION ORIENTED SCHEME
5. OTHER SCHEMES
EQUITY SCHEMES
In this the investment is primarily done on Equity and Equity related investments i.e. in stock market.
The risk is higher than the Debt Schemes as the investment return is arrived from value of the underlying stocks
This type of schemes are better suited for the people with high risk appetite and long term investment objective.
Small, Mid and Large Cap Funds
The stocks are classified as Small Cap, Mid Cap, Large Cap based on the market capitalisation.
- Large Cap – Top 100 companies in stock market.
- Mid Cap – 101 to 250 companies in stock market.
- Small Cap – 251 and above Companies in stock market.
| Multi Cap Fund | Invests in combination of Small, Mid, Large Cap funds with its portfolio of at least 65% investment in equity & equity related instruments. |
| Large Cap Fund | At least 80% investment in large cap stocks. |
| Large & Mid Cap Fund | At least 35% investment in large cap stocks and 35% in mid cap stocks |
| Mid Cap Fund | At least 65% investment in mid cap stocks |
| Small cap Fund | At least 65% investment in small cap stocks |
Other Equity Schemes
| Value Fund | These are funds in which the investment is done on low value stocks which are expected to perform well in the future. This is a very high risk scheme as identification of a valuable stock is hard. In this minimum 65% is invested in equity. |
| Contra Fund | In Contra Fund the investment is done on the under valued stocks that are doing bad because of the present bear market and will do better in the future. These are very high risk scheme as there is a chance of even losing a capital with a wrong choice of fund fund. In this minimum 65% of fund is invested in stocks. |
| Sector Based Fund | Investment is made in particular sector as per schemes objective. Minimum 80% of fund is invested in the particular sector. |
| ELSS | In this scheme minimum 80% of the investment is made in equity. This scheme has a lockin period of 3 years. Investment upto 1.5 Lakh is having a tax benefit under 80C of Income Tax Act. |
As per SEBI guidelines a fund house can either provide Value Fund or Contra Fund but not both.
Debt Schemes
In this scheme most of the funds are invested in bonds and Debt related securities.
Based on the tenure of the securities in the scheme the classification is made as follows
| Maturity period of securities invested | Funds |
| 1 day | Overnight Fund |
| upto 91 days only | Liquid Fund |
| 3 months – 6 months | Ultra Short Duration Fund |
| 6 months- 12 months | Low Duration Fund |
| 1 year – 3 years | Short Duration Fund |
| 3 years – 4 years | Medium Duration Fund |
| 4 – 7 years | Medium to Long Duration Fund |
| More than 7 years | Long Duration Fund |
| Investment across duration | Dynamic Bond |
| Investment in Money Market instruments having maturity upto 1 Year | Money Market Fund |
Based on the fund management strategies the Debt Funds are classified as follows
| Corporate Bond Fund | Minimum 80% investment in corporate bonds only in AA+ and above rated corporate bonds |
| Credit Risk Fund | Minimum 65% investment in corporate bonds, only in AA and below rated corporate bonds |
| Banking and PSU Fund | Minimum 80% in Debt instruments of banks, Public Sector Undertakings, Public Financial Institutions and Municipal Bonds |
| Gilt Fund | Minimum 80% in G-secs, across maturity |
| Gilt Fund with 10 year constant Duration | Minimum 80% in G-secs, such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is equal to 10 years |
| Floater Fund | Minimum 65% in floating rate instruments (including fixed rate instruments converted to floating rate exposures using swaps/ derivatives) |
Hybrid Funds
The Funds are invested in both Debt and Equity securites in this sceme.
As per SEBI, Hybrid Funds are having seven sub classification.
| Fund | Investment |
| Conservative Hybrid Fund | 10% to 25% investment in equity & equity related instruments; and 75% to 90% in Debt instruments |
| Balanced Hybrid Fund | 40% to 60% investment in equity & equity related instruments; and 40% to 60% in Debt instruments |
| Aggressive Hybrid Fund | 65% to 80% investment in equity & equity related instruments; and 20% to 35% in Debt instruments |
| Dynamic Asset Allocation or Balanced Advantage Fund | Investment in equity/ debt that is managed dynamically (0% to 100% in equity & equity related instruments; and 0% to 100% in Debt instruments) |
| Multi Asset Allocation Fund | Investment in at least 3 asset classes with a minimum allocation of at least 10% in each asset class |
| Arbitrage Fund | Scheme following arbitrage strategy, with minimum 65% investment in equity & equity related instruments |
| Equity Savings | Equity and equity related instruments (min.65%); debt instruments (min.10%) and derivatives (min. for hedging to be specified in the SID) |
SOLUTION ORIENTED FUNDS
This fund have a specific objective to cater for. Thus the tenure and investment securities are selected based on the objective of the scheme.
For example there is a Retirement fund, objective of which is to give lump sum or monthly income after the retirement of investor.
OTHER FUNDS
There is no specific definition for this scheme. It has a mix of investment options that caters to the need of the investor.
Index Fund
Investment done on purely based on the market Index as a whole i.e., invests in top companies in stock market. Fund manager does not decides on the stocks invested.
Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)
ETF is a Stock that follows exactly the index value, thus you can directly purchase ETF from stock market without a fund manager.
This is held in Demat Account. These are passively managed funds, thus the fund manager fee is lesser compared to other schemes.
Funds of Funds
In this funds are invested various mutual fund schmes to mitigate the risk lying with particular AMC.
These are the types of Mutual Funds available for subscription in the market. You should consider chooosing a right scheme with respect to your risk appetite, tenure and objective of investment.
For queries and feedback kindly write a comment to improve ourself.
May I simply say what a comfort to discover somebody who genuinely knows what they are talking about over the internet. You actually understand how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More people ought to check this out and understand this side of the story. I cant believe you arent more popular because you surely possess the gift.